A common query among dog owners is understanding the aging process of their canine companions. A surprising fact is that one in five dogs will live to be 15 or older, highlighting the importance of understanding their aging process.
How Many Dog Years Are in a Year
The popular belief that one dog year equals seven human years is an oversimplification. The actual aging process of dogs is influenced by several factors including breed, size, and health conditions.
Understanding the concept of dog years and the factors that affect their aging is crucial for providing proper care and attention. By exploring the truth behind dog years, we can better appreciate the needs of our dogs as they age.
The Science Behind How Many Dog Years Are in a Year
The science behind dog aging reveals a more nuanced picture than the traditional 7:1 ratio. While this ratio has been a long-standing rule of thumb for converting dog years to human years, it oversimplifies the complex process of canine aging.
Dog aging is influenced by a multitude of factors, including breed, size, diet, and health conditions. For instance, larger breeds tend to have shorter lifespans compared to smaller breeds, a factor not accounted for in the simplistic 7:1 ratio.
Debunking the 7:1 Myth
The 7:1 ratio is believed to have originated from the idea that dogs live for about 10 years on average, while humans live for about 70 years. However, this calculation does not take into account the varying rates at which dogs mature and age.
Research has shown that dogs mature more quickly than humans, with the first two years of a dog’s life being equivalent to a much larger number of human years. After this initial period, the rate of aging slows down.
Factors Affecting Dog Aging
Several factors contribute to the aging process of dogs, including size, breed, genetics, diet, and health conditions. For example, larger breeds tend to age more rapidly than smaller breeds. Additionally, certain breeds are prone to specific health issues that can affect their lifespan.
| Factor | Impact on Dog Aging |
|---|---|
| Size | Larger breeds tend to age more rapidly and have shorter lifespans. |
| Breed | Certain breeds are prone to specific health issues that can affect their lifespan. |
| Diet and Nutrition | A balanced diet can contribute to a healthier, potentially longer life. |
| Health Conditions | Chronic health issues can significantly impact a dog’s quality of life and lifespan. |
By understanding these factors and using canine age charts or dog year calculation methods, dog owners can gain a more accurate insight into their dog’s age in human years.
Modern Dog Age Calculation Methods
Modern approaches to dog age calculation consider multiple factors, moving beyond the simplistic traditional ratio. This shift acknowledges the complexity of canine development and the various influences on a dog’s aging process.
The traditional method of calculating dog years has been largely debunked, and new, more nuanced methods have emerged. These modern dog age calculation methods take into account various factors, including size and breed, to provide a more accurate conversion of dog years to human years.
Size and Breed Considerations
One of the key factors in modern dog age calculation is the consideration of size and breed. Research has shown that larger breeds tend to age more quickly than smaller ones. This is because larger dogs have more cells, which can lead to a higher rate of cell division and, consequently, a greater risk of genetic errors that can contribute to aging and age-related diseases.
For example, a Great Dane is considered a senior dog at around 5-6 years, while a Chihuahua may not be considered senior until it is 10-12 years old. This disparity highlights the importance of breed and size in determining a dog’s age in human years.
| Breed Size | Average Lifespan | Senior Age |
|---|---|---|
| Small (under 20 lbs) | 12-15 years | 10-12 years |
| Medium (21-50 lbs) | 10-14 years | 7-10 years |
| Large (51-90 lbs) | 8-12 years | 5-7 years |
| Giant (over 90 lbs) | 6-10 years | 5-6 years |
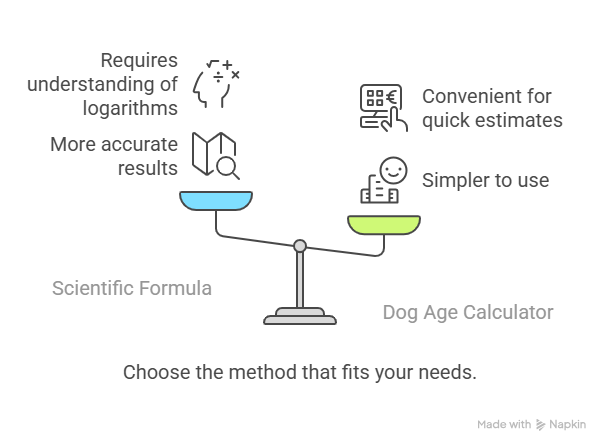
The Scientific Formula for Dog Age
A more scientific approach to calculating dog age involves using a formula that takes into account the dog’s size and breed. One such formula is based on the dog’s weight and age, providing a more accurate conversion to human years.
The formula is as follows: human age = 16 * ln(dog age) + 31. This formula is based on the natural logarithm of the dog’s age and provides a more nuanced estimate of a dog’s age in human years.

Using a Dog Age Calculator
For those who prefer a simpler approach, dog age calculators are available online. These calculators typically ask for the dog’s age, breed, and size, and then provide an estimate of the dog’s age in human years.
Using a dog age calculator can be a convenient way to determine a dog’s age, especially for those who are unsure about the more complex formulas or factors involved in calculating dog years.
Conclusion
Understanding a dog’s age in human years is crucial for providing the best possible care. As we’ve seen, the traditional method of calculating dog years is no longer considered accurate. Instead, modern methods take into account factors such as breed, size, and health conditions to provide a more precise calculation.
Using a dog years calculator is an effective way to determine a dog’s age in human years. These calculators consider the various factors that influence a dog’s aging process, giving owners a better understanding of their dog’s needs. By knowing how to calculate dog years accurately, owners can tailor their care to meet their dog’s specific requirements, ensuring they lead happy and healthy lives.
By adopting these modern methods, dog owners can gain a deeper understanding of their canine companions and provide the care and attention they need at different stages of their lives.





